Copyright 2020 - 2021 irantour.tours all right reserved
Designed by Behsazanhost
First Time in IRAN
Where To Stay in IRAN
What type of traveller are you?
What to see in IRAN
Tours And Activities
Qanat
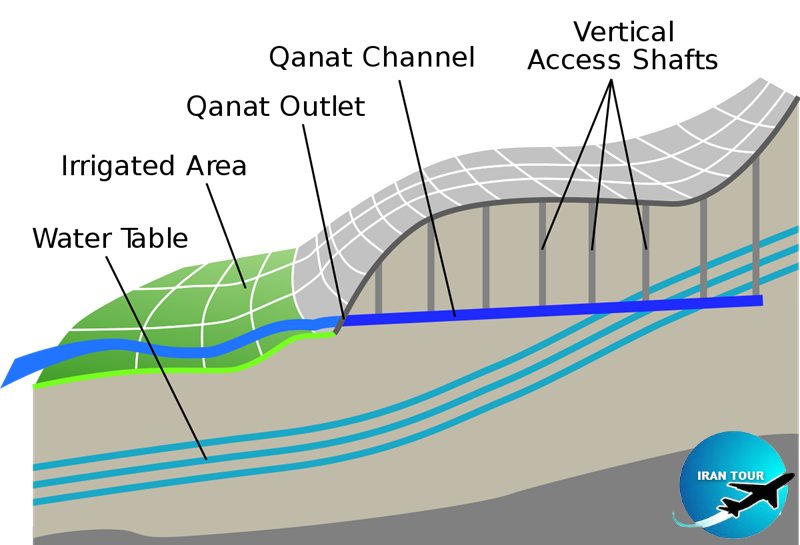
Aqueduct (Qanat) or underground canals is the most important invention and amazing achievement of Iran's hot desert habitant for irrigating fields and houses and resisting the dry desert of Iran.The Qanats are the largest and longest man-made to sustain life on earth. Qanat is one of the most important masterpieces of Iranian engineering and architecture also is one of the most important and valuable inventions of Iran's Hydraulic engineering. The construction of Qanats represents the history of a great civilization that has been living in this area for centuries and has been the source of various developments. Qanat has technical and aesthetic principles. It represents the peak of Iranian art development not only on earth but also underground. This complicated and technical technique is the source of various buildings related to it.
 |
Public and charitable buildings such as:
Bathroom
Ab Anbar (is a traditional reservoir or cistern of drinking water in Greater Iran).
These public buildings show the strong relationship between the value of water and the religious beliefs of Iranians. Qanat was introduced as the source of life in old cities. It has had a very important role to build urban structures and expand cities. But the exact date of the invention is not clear. But some believe that it was about six thousand years ago. In any case, this irrigation technique has watered the people for centuries
Qanat
A qanat or
 |
Names
Qanat is an Arabic word that means "channel" its Persian word for "qanat" is "
Technical features
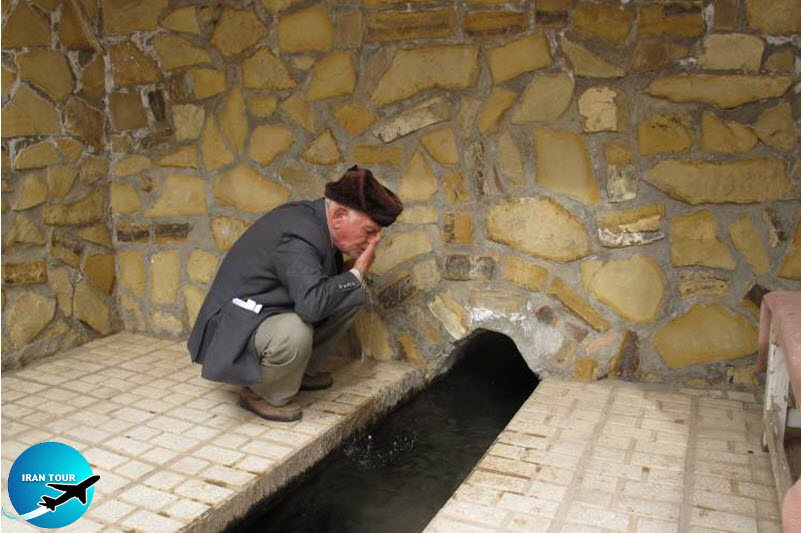
The original ancient engineered design of the Qanat and its multiple aligned boreholes are for controlling the desert endorheic basin flooding. Qanats are constructed and connected with a series of gently sloping tunnels and vertical shafts. Qantas efficiently deliver large amounts of water to the surface without pumping. The water drains by gravity, typically from an upland aquifer, with the destination lower than the source. Qanats transport the water over long distances in hot dry climates with the lowest vaporization.
The first step in making a
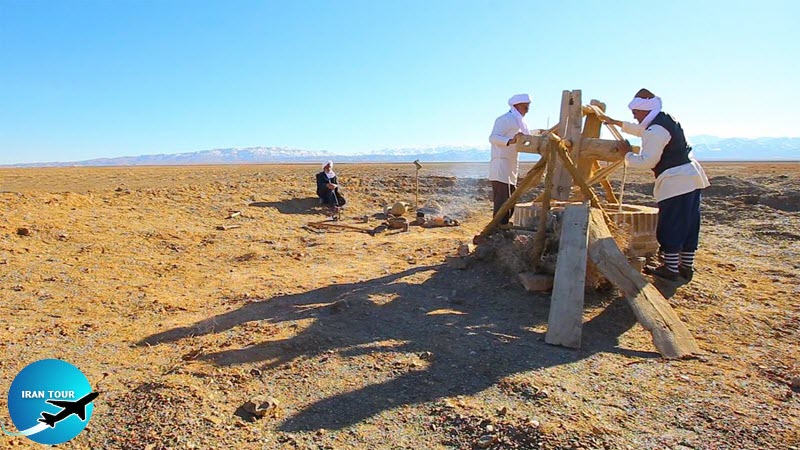
Usually, there accumulates a ring of soil around the shaft on the surface. So, looking from the air, a row of wells will be visible. The
 |
Maintenance of Qanats
After digging the Qanat by the worker, It does not mean that their job is over. They clean and repair the corridors of qanat all the time. It should do to keep the water flowing or even increase the qanat water discharge. They have some special tools and methods to examine the integrity and health of the qanat structure. This chapter takes up the traditional methods of maintaining a qanat by best shape. some of these methods are:
extending its gallery to the area of water, containment, deepening, branching, dredging, lining, etc.
The people who carry out these activities are called Moqannies. They also have special cleaning tools, Oxygen tests, and other repairs.
 |
Ownership & Distribution of Water in Kariz Systems
Ownership of these Qantas depends on a variety of factors In some cases, Qanat passes in different lands, therefore, there are a number of different owners that its water is bought and sold by them. In many cases,
Undoubtedly, qanats have been one of the most important factors in the survival of humans. In addition, there would be no oasis to later become large cities such as Hamedan, Qazvin, Neyshabur, Kerman, Yazd, and other smaller cities and towns. In the mentioned regions, there could not be any cultivated land either.
From thousands of years ago, there have been different and special laws for distributing
Although with new irrigation systems, Qanats do not have their past validity, they are still considered as one of the most important and effective agricultural factors in some desert areas.
Finally,
 |
The most important Iranian Qanats
At the 40th UNESCO World Heritage Summit in Istanbul, July 2016, Eleven Iranian Qanats were registered. 11 Iranian Qanats with different technologies dating back to more than 2500 years registered at UNESCO World Heritage. The most important features recorded for Iranian aqueducts are:
 |
- Being Unique or exceptional
- A cultural tradition
- An outstanding example of architecture or technology that represents an important stage in human history.
1- Ghassabeh Gonabad Qanat: is Iran's deepest Qanat, its main Shaft is 350 meters deep.
2- Ferdows Village Qanat: in south Khorasan is belongs to the Sassanid period. This large Qanat consists of 16 smaller ones and 2 springs.
3- Zarach Yazd Qanat: is the longest Iranian qanat with a length of 100 km and 2115 wells.
4- Moon Qanat: Ardestan has the only two-level Qanat in Iran that was built about 800 years ago. On each floor of this Qanat, the water flows independently so that water does not penetrate into another.
5- Hassan Abad Mehriz Qnat in Yazd province: dating back to 700 years ago.
6- Wazavan Qanat in the city of Wazan and Mazdabad Qanat in the city of Meymand.These two Qanat have underground dams.
7- Jupar Kerman Qanat Gohar Riz at
8- Ebrahim Abad Abad Arak Ghana: is one of the oldest ones in Iran.
9- Ghasemabad and Akbarabad Qanats Bam, Kerman: were registered in UNESCO because they were twins.
- Details
- Category: What to see in IRAN